ACCESS CONTROL
접근제어
Types of access control
- MAC (Mandatory Access Control) / DAC (Discretionary Access Control): MAC 또는 DAC는 데이터 객체(예, 파일)를 중심으로 접근 권한을 제어하는 방법이다. MAC는 관리자 또는 정책에 따라 데이터 객체의 접근 권한을 설정하지만, DAC는 데이터 객체의 소유자가 자유재량(discretion)을 가지고 권한을 통제할 수 있다(예, Unix 파일 시스템).
- IBAC (Identity-based Access Control): IBAC은 사용자를 기준으로 권한을 통제하는 방법으로 가능한 모든 기능에 대해 개별적으로 권한을 부여한다. 따라서, 사용자가 적은 시스템에서는 쉽게 구현할 수 있지만, 사용자의 수가 늘어남에 따라 관리가 어려워지게 된다.
- RBAC (Role-based Access Control): RBAC은 개별 권한을 역할 (role)로 묶고, 이 역할을 개인에게 부여하여 IBAC의 제약 조건을 극복한다. RBAC의 각 역할이 계층 구조를 갖는 경우에는 이를 HRBAC (Hierarchical RBAC)이라고 한다.
- ABAC (Attribute-based Access Control): ABAC은 RBAC보다 정교하게 접근 제어를 할 수 있는 방법으로 사용자, 기능, 환경 등 다양한 요소의 속성을 기준으로 한 정책에 따라 권한이 결정된다.
Designing an Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) System
intro
role 에 대한 몇가지 기본 의미론과 역할을 정의하는 일련의 속성, 운영자 및 작업이 있습니다.
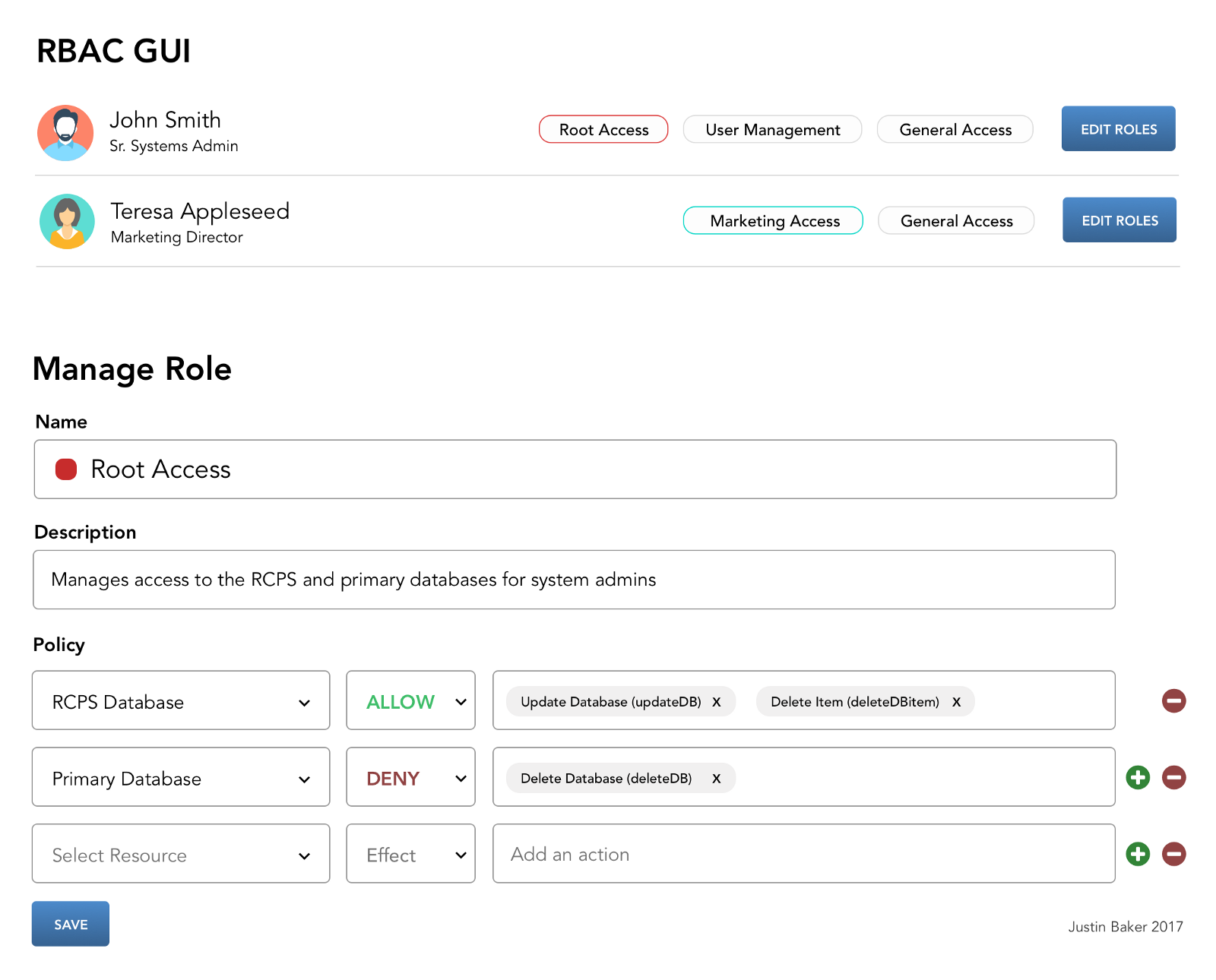
Defining a Role (역할 정의)
A role should have five semantic components:
- Name — 역할을 식별하는 사람이 읽을 수 있고 비즈니스 친화적인 방법(a human readable and business-friendly way to identify a role)
- Description — 명확하게 정의된 역할의 목적(the role’s purpose, clearly defined)
- Tags — 여러 역할을 관리하는데 중요한 의미를 가짐(important for managing multiple roles and creating roles to manage to roles)
- Assignments — 개인 또는 개인의 그룹에 역할 할당 (assigning roles to individuals or groups of individuals)
- Policies — 역할에 할당 된 특정 규칙및 권한( specific rules and permission sets assigned to a role)
Defining a Policy (정책 정의)
A policy has one primary component:
- Array of Statements — 정책은 많은 statements을 가질 수 있습니다. 정책을 정하고 여러 역할에 걸쳐 정책을 재사용할 수 있어야 한다. 즉, 정책은 특정 사용 권한 규칙의 모음이다.( a policy can have many statements. You should be able to save policies and re-use them across multiple roles. In other words, a policy is a collection of specific permission rules.)
Defining a Statement
A statements has three components:
- Resource — 대상 기능, 환경 또는 작업(the targetted feature, environment, or operation)
- Effect — 허용 또는 거부(typically “Allow” or “Deny”)
- Action — 동작 (a resource can have many actions, like deleteUser, addUser, modifyUser. These actions should have human readable names, like “Delete a User” for “deleteUser”. This is essential when you get into more complex actions, like “Modify Image Upload” for “imgUploadMod”.)
omt: 우리는 이 Action을 Apache Shiro의 [[Apache_Shiro_WildcardPermission]]{WildcardPermission} 을 사용하여 표현하고 있다.
{
"effect": "deny",
"resources": [
"prod/primaryDB/*"
],
"actions": [
"deleteDB"
]
}
Mapping Roles
개별 사용자에게 여러 역할을 지정할 수 있어야 합니다. 이상적으로는 이러한 역할을 만들어 개별 사용자 또는 사용자 그룹에 연결할 수 있는 명확한 UI 가 있어야 한다. (You should be able to assign multiple roles to an individual user. Ideally, you would have a clear user interface that allows you to build these roles and attach them to individual users or groups of users.)
Avoiding Technical Debt
대기업은 시간이 지남에 따라 수백 수천가지 role을 수행하는 것이 일반적이다. 직관적인 GUI를 사용하면, 부채를 관리하고 역할을 최신 상태로 유지하며 시스템을 안전하게 유지할 수 있다. (It is very common amongst large companies to accrue hundreds or thousands of roles over time. Having an intuitive GUI lets you manage this debt, keep your roles up-to-date, and keep your system secure.)
우리 접근 제어의 문제점
- 행위에 대한 범위를 지정할 수 없다.
- 행위의 계층이 자동화되있지 않다.
omt : only my think!
출처1: https://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/access-control
출처2: https://hackernoon.com/designing-an-enterprise-role-based-access-control-rbac-system-96e645c659b7